What is De-Essing, and How to Use it to Process Vocals
De-essing is an essential technique in audio production, especially when processing vocals. It involves reducing or removing the harsh "s" sounds, known as sibilance, that can occur during recording. This sibilance is often more pronounced in recorded audio than in natural listening situations due to the close proximity of the microphone to the mouth and the sensitivity of microphones to high-frequency sounds. For music producers and audio engineers, de-essing is a crucial step in ensuring that vocals sound smooth and pleasant in the final mix. In this blog post, we'll explore what de-essing is and how music producers use it to process vocals effectively.
Understanding De-essing
De-essing targets the sibilant frequencies, which typically range from 2 kHz to 10 kHz, depending on the individual's voice and the recording conditions. These frequencies can become overly prominent in a vocal track, leading to a piercing or hissing sound that can be distracting or even uncomfortable for listeners. The goal of de-essing is to attenuate these frequencies only when they become problematic, without affecting the overall quality and clarity of the vocal performance.
Techniques for De-essing
There are several methods that music producers can use to de-ess vocal tracks, including:
Dynamic EQ: Unlike a static EQ that affects the sound at all times, a dynamic EQ only reduces the level of the sibilant frequencies when they exceed a certain threshold. This method allows for more precise control and preservation of the vocal's natural timbre.
Multiband Compression: This technique involves compressing only the frequency range where sibilance occurs. By setting a compressor to act on a narrow band around the problematic frequencies, producers can reduce sibilance without impacting the rest of the audio spectrum.
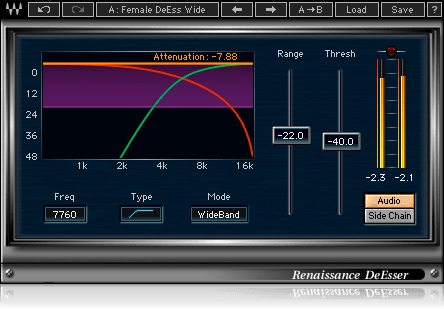
De-esser Plugins: There are many dedicated de-esser plugins available that are specifically designed to identify and reduce sibilance. These plugins often offer user-friendly interfaces and presets that can simplify the de-essing process for producers.
How to Use De-essing Effectively
Identify the Problematic Frequencies: The first step is to identify the frequency range where the sibilance is most prominent. This can vary significantly between different voices and recording setups.
Set the Threshold: The threshold determines when the de-essing effect will be triggered. It should be set so that the de-esser only activates when the sibilance is too strong, without affecting the rest of the performance.
Choose the Right Technique: Depending on the specific needs of the vocal track and the desired outcome, producers may choose dynamic EQ, multiband compression, or a dedicated de-esser plugin to tackle sibilance.
Listen in Context: It's important to listen to the processed vocal track in the context of the full mix. De-essing settings that sound good in solo mode may need adjustments when other instruments are introduced.
Conclusion
De-essing is a critical tool in the music producer's toolkit, allowing them to polish vocal tracks and achieve a professional-sounding mix. By carefully applying de-essing techniques, producers can ensure that vocals sit perfectly in the mix, providing a pleasing listening experience without distracting sibilance. Whether you're a seasoned audio engineer or a budding music producer, mastering the art of de-essing is an essential step in creating high-quality music productions.