Resonance Revolution: Mastering the Mystique of Filter Resonance in Sound Design and Music Production
In the realm of audio and music production, filters are essential tools for shaping sound. Among the various filter parameters, resonance is a captivating and often misunderstood aspect. In this post, we will embark on a journey through the world of filter resonance, exploring its fundamentals, applications, creative uses, and the role it plays in sculpting unique sonic landscapes.
I. Unpacking the Essence of Filter Resonance
Before we dive into the practical applications of filter resonance, let's start by understanding what it is and how it works.
Filters in Audio
Filters are audio processors that modify a signal by allowing or attenuating certain frequency components. They are commonly used in synthesizers, effects processors, and recording equipment to shape the tonal characteristics of audio.
Resonance Defined
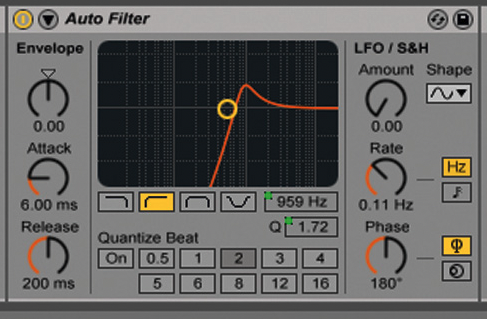
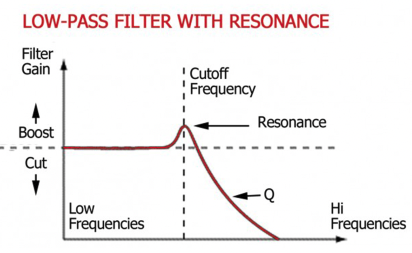
Resonance is a filter parameter that refers to the emphasis or boost of frequencies near the cutoff frequency (the point at which filtering begins). When resonance is applied, it creates a peak in the frequency response curve, resulting in a distinctive and often pronounced tonal effect.
II. The Anatomy of Filter Resonance
To wield the power of filter resonance effectively, it's essential to break down its key components.
Cutoff Frequency
The cutoff frequency is the point at which the filter starts affecting the signal. Below the cutoff frequency, frequencies are attenuated, while those above are allowed to pass through unaffected.
Resonance Amount
Resonance amount controls the intensity of the peak created near the cutoff frequency. Higher resonance settings result in a more pronounced boost.
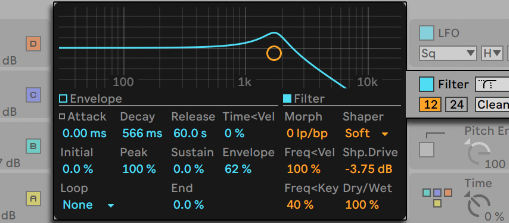
Filter Types
Different filter types, such as low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and notch filters, exhibit resonance differently. Each filter type emphasizes or attenuates different portions of the frequency spectrum.
III. Practical Applications of Filter Resonance
Filter resonance has a wide range of applications in music production and sound design:
Emulating Acoustic Instruments
Filter resonance can be used to emulate the natural resonance characteristics of acoustic instruments. For example, applying resonance to a low-pass filter can replicate the warm, mellow quality of a violin's resonance.
Sound Design
Sound designers use resonance to create unique textures and effects. By modulating resonance parameters, they can craft evolving, otherworldly sounds that are essential in film, video games, and electronic music.
Synthesis
Resonance is a fundamental element in subtractive synthesis. It allows synthesists to sculpt evolving timbres and explore new sonic territories.
Percussive Sounds
Filter resonance can be applied to percussive sounds like drum hits to give them a distinct character and resonance, making them stand out in a mix.
IV. Creative Sound Sculpting with Filter Resonance
Beyond its utilitarian applications, filter resonance offers creative possibilities that can transform your soundscapes:
Sonic Whistles and Howls
By cranking up resonance on a low-pass filter, you can create eerie, whistling, or howling effects that evoke feelings of suspense and tension in your music or sound design.
Talking Filter
With the right modulation, filter resonance can mimic the human vocal tract, producing vowel-like or formant-like sounds that "talk" or "sing." This technique is popular in synthesizer-based music.
Enveloped Filter Sweeps
Applying an envelope generator to the resonance parameter can create dramatic, evolving filter sweeps that add movement and intensity to your music.
Dub-Style Effects
Filter resonance is a key ingredient in dub music, where it's used to create "dub sirens" and "wah-wah" effects that define the genre's iconic sound.
V. Practical Tips for Using Filter Resonance
As you explore filter resonance in your music production, keep these practical tips in mind:
Start with Low Resonance
When using resonance, start with a low or moderate setting and gradually increase it. High resonance settings can be extreme and may result in unwanted distortion or piercing tones.
Experiment with Different Filter Types
Each filter type (e.g., low-pass, high-pass, band-pass) interacts with resonance differently. Experiment with various filter types to find the one that best suits your creative vision.
Modulation Is Key
Modulating resonance over time can yield dynamic and evolving effects. Use envelope generators, LFOs, or automation to shape the resonance parameter.
EQ Considerations
Be mindful of the overall tonal balance when applying resonance. Boosting specific frequencies with resonance can lead to frequency imbalances in your mix.
Listen Critically
Regularly A/B test your audio with and without filter resonance to ensure it enhances your sound rather than detracting from it.
VI. Filter Resonance in Different Music Genres
Filter resonance finds its place in various music genres, each harnessing its unique characteristics:
Electronic Music
In genres like techno, house, and trance, filter resonance is a staple for creating evolving synth textures, sweeps, and signature filter-driven soundscapes.
Rock and Pop
Filter resonance can add character to electric guitar tones, making them stand out in rock and pop mixes. It's also used in vocal processing and effects.
Experimental and Ambient
Experimental and ambient musicians often push the boundaries of filter resonance, using it to create ethereal, evolving soundscapes that take listeners on sonic journeys.
VII. The Future of Filter Resonance
As music production technology continues to advance, the future of filter resonance holds exciting possibilities:
Advanced Modulation
Future audio processors may offer even more sophisticated modulation options for filter resonance, enabling musicians to create intricate and evolving sonic textures.
Integration with AI
Artificial intelligence and machine learning may be employed to analyze audio material and suggest optimal resonance settings, speeding up the sound design process.
Visualization Tools
Improved visualization tools may help producers and sound designers better understand how resonance affects the frequency spectrum, making it easier to achieve desired sonic results.
Conclusion
Filter resonance is a captivating and versatile tool that plays a vital role in music production and sound design. Whether you're shaping the timbre of an instrument, creating unique textures, or crafting dramatic sonic effects, resonance is your ally in the quest for sonic expression. By understanding its principles, experimenting creatively, and applying practical tips, you can unlock the full potential of filter resonance and let it become your sonic paintbrush for crafting captivating and expressive audio. So, embrace the art of resonance, and let your creativity soar in the ever-evolving world of sound.